What is a diploma?
As far as pre-university courses in Malaysia go, a diploma is one of the most popular choices. This can be largely attributed to its learning structure that emphasises practical skills in a specialised field.
Typically spanning two to two-and-a-half years, a diploma enables you to jump straight into the workforce upon completion. To enrol, candidates generally need to have at least passed their Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM) exams or an equivalent, although specific entry requirements may vary based on the course and institution.
Students are often assessed via a combination of coursework, examinations, assignments and presentations, allowing for a more holistic evaluation of their knowledge and skills. The cost of pursuing a diploma in Malaysia can vary widely (between RM15,000 and RM50,000) based on factors such as the institution, course of study and duration.
In 2022, the Department of Statistics Malaysia reported a 5.5 per cent year-on-year growth in the number of diploma graduates in Malaysia. Out of 5.92 million graduates, 46.1 per cent of them are diploma graduates – a testament to the continued popularity of this type of programme.
What subjects can you choose for a diploma?
The subjects in a diploma programme generally cover the basics of your chosen field, as well as their practical applications.
Whether it’s business, engineering, healthcare or the arts, you will learn the fundamental theories and get hands-on experience.
This mix will help you get a foundational understanding of your field of study and prepare you for future career opportunities.
Example subjects by diploma type
| Diploma type | Subjects |
|---|---|
| Diploma in Hotel Management |
|
| Diploma in Business |
|
| Diploma in Mass Communication |
|
| Diploma in Information Technology (IT) |
|
| Diploma in Education |
|
Diploma vs other pre-university programmes
| Criteria | Diploma | Foundation | STPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | 24 - 30 months | 12 months | 18 months |
| Structure | Focuses on a specific field of study, with greater emphasis on learning practical skills that boost one’s employability upon graduation | Tailored to degree courses offered by the university and a combination of compulsory, elective and general studies subjects | Modular format that continually assesses students of three six-month-long semesters. Beyond written exams, students are assessed via field study, projects and practical work |
| Assessment | Mix of assignments, practical assessments, coursework and examinations | Mix of coursework, exams, quizzes and final assessments | School-based assessment (20-40%), centralised examinations (60-80%) at the end of each term and co-curricular activities (10%) |
| Recognition | Recognised for degree acceptance at the university offering the diploma. Credit transfer may be applicable to other institutions | Recognised by the university that provides the programme and some other private universities (may vary from institution to institution) | Recognised by all local public universities, local private universities and over 2,000 foreign universities |
| Entry requirements | Course-specific requirements | Varies by university | Entry to public universities requires a minimum CGPA of 2.00, with grades of C and above in three subjects, including general studies. Entry requirements for local private universities and foreign universities vary according to institution |
| Number of subjects | Varies by course | Varies by course | 4 - 5 |
| Criteria | A-Levels | American Degree Transfer Program (ADTP) | WesternAustralian Matriculation (AUSMAT) | Canadian International Matriculation Programme (CIMP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | 14 - 24 months | 24 months | 7 - 10 months | 12 - 15 months |
| Structure | Has two levels called AS and A2, which foster critical thinking and in-depth knowledge of chosen subjects | Broad-based, learning-driven education | Assignment-based with continuous assessment | Interactive learning focus, with a progressive accumulation of marks |
| Assessment | Final examinations at the end of each level | Mix of exams, coursework, assignments, presentations, quizzes and research papers | 50% coursework and 50% exams | 70% coursework and 30% final examinations |
| Recognition | Widely recognised by local and international institutions | Recognised by American universities | Recognised by local and international institutions | Recognised by local and international institutions |
| Entry requirements | Subject-specific requirements that depend on the course | Completion of approximately 60 credits | Varies by university | Varies by university |
| Number of subjects | 3 - 4 | 20 | 5 | 6 |
- Fast facts about diploma studies
-
Many diploma programmes require only a minimum of three credits in SPM or equivalent, compared to other pre-university courses requiring five credits or more.*
-
Diploma programmes usually go for two to two and a half years.
-
Students are usually assessed via a mix of assignments, practical assessments, coursework and examinations.
*Requirements vary from institution to institution, so it is recommended to check with your desired college/university before proceeding.
Benefits of studying a diploma
-
Accelerates the completion of a bachelor's degree programme
Many institutions allow diploma holders to enter directly into the second year of a bachelor's degree programme, enabling them to skip the first year. However, this can vary depending on the specific policies of each institution. -
Can be further specialised with majors and minors
Some diploma courses offer majors and minors, allowing for an even more specialised education. For instance, a Diploma in Mass Communication might offer a major in public relations. Minors provide a secondary specialisation and may require fewer modules to complete. -
Qualifies you for entry into the workforce
A diploma certificate is valuable in the job market as it enables you to enter the workforce without any further education. However, note that the starting salary would be lower as most jobs require or prefer graduates with a bachelor's degree or higher. According to the 2022 Salaries and Wages Survey Report by the Department of Statistics Malaysia, a degree holder earns 62 per cent more than a diploma holder on average. -
Dual internship experience
Diploma courses often require you to do an internship. Completing a diploma and pursuing a bachelor's degree afterwards means you may get double the industry exposure, as an internship is sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree programme. This dual internship experience can boost your practical skills and your employability. -
Enhanced employability in the fresh graduate job market
With a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical skills and real-world experience gained through diploma studies and internships, graduates are better positioned to stand out in the fresh graduate job market.
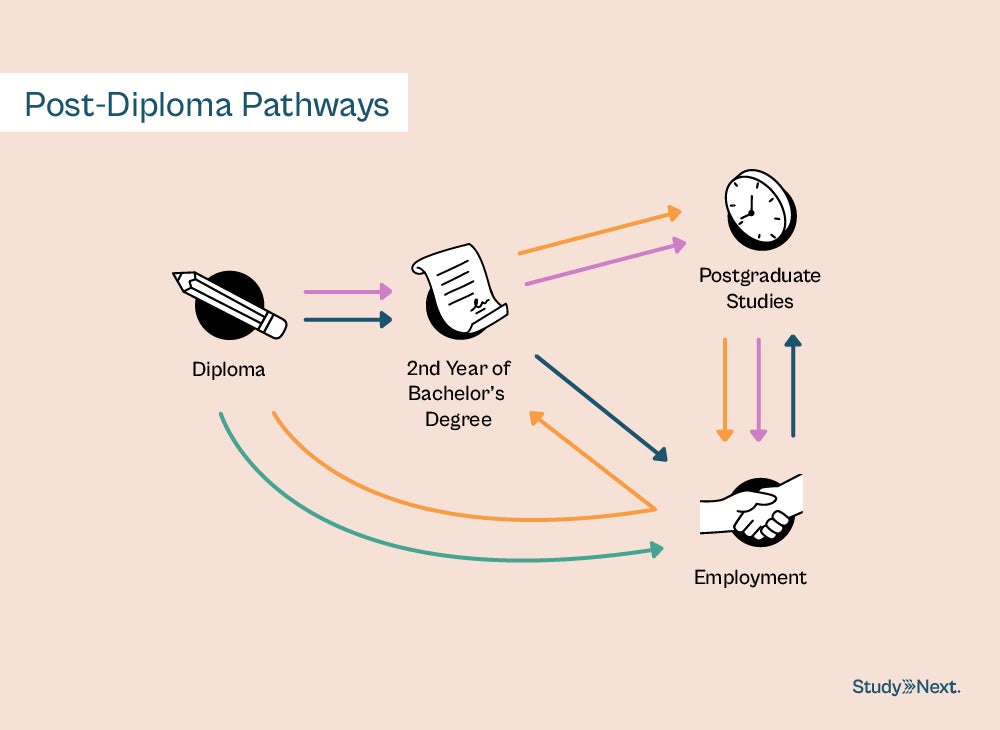
Post-diploma pathways
Getting a diploma can open up many education and career opportunities.
On the career front, diploma holders can enter the workforce directly, securing entry-level positions in various industries. You may still resume your studies later to boost your qualifications. Some also choose to enter the workforce earlier with a diploma to gain a few years of working experience before continuing their educational pursuits.
For those aspiring to pursue a degree, a diploma can expedite the process of getting a bachelor’s degree, as you can immediately skip forward to the second year of your bachelor’s studies. With a bachelor’s degree, you can usually command a higher salary.
Those looking to deepen their knowledge and specialise in a particular field may want to continue with postgraduate studies after completing their bachelor’s. Similarly, you can work for a few years before returning to this.
Who should get a diploma?
If you have a strong passion or a clear idea of what you want to do career-wise, a diploma may be one of the most ideal pre-university options for you. It caters to those who wish to delve into a particular field of study, while acquiring industry-relevant, practical skills that make you workforce-ready.
While both a diploma and STPM (Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia) are similar in that they take longer to complete than other pre-university courses, one notable distinction is that completing a diploma potentially enables you to enter the second year of a bachelor's degree programme, bypassing the first year. Upon completion of STPM, you will have to start from the first year of the course to get a bachelor’s degree.
A diploma is suitable for students who are decisive about their career path and wish to enter the workforce sooner.
It's worth mentioning that the specialised nature of a diploma may limit the range of viable bachelor's degree programmes or career options available to you later.
How to apply for a diploma
Aspiring students should identify the course and institution that fits their academic and career goals. Then, they can either consult an education counsellor from the institution to find out more or browse through the diploma courses available on StudyNext.
When applying for a diploma, students may need to show proof of English proficiency via the Pearson Test of English (PTE Academic or PTE Academic Online), IELTS or TOEFL results. Some institutions may also conduct interviews or aptitude tests as part of the selection process.
After your application is submitted and reviewed, you will receive an offer of admission if you are successful. This offer letter will detail the next steps, including payment of fees, enrolment confirmation and registration for classes.
Diploma courses in Malaysia
Many of Malaysia's universities offer diploma courses. To help you get a feel for some of the different types of programmes, here are a few to consider:
- HELP University
HELP University has an illustrious history when it comes to diploma offerings. It was established in 1986 and in that same year, it became the first institution outside of the United Kingdom to offer the University of London external programmes. Today, you can pursue a diploma in areas such as business, communication and information technology at HELP University. - MARA University of Technology
MARA University of Technology (Universiti Teknologi MARA or UiTM) is among the top 100 universities in Asia according to the QS Asian University Rankings, coming in at #98 in 2024. This public institution boasts an impressive variety of diploma courses, offering a whopping 59 programmes across 17 faculties. - Sunway University
Since 2017, Sunway University has achieved the lofty status of Premier Digital Technology University, an award jointly developed by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) and Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) that recognises top talent and future leaders in digital tech. Sunway University offers diploma courses across its arts, hospitality and service management, and medical and life sciences schools. - University of Technology Malaysia
Ranked 37th in the QS Asian University Rankings 2024, the University of Technology Malaysia (UTM) is one of the leading public institutions in Malaysia known for its diverse variety of courses. It offers diploma programmes in various engineering disciplines, as well as technology management, accounting, quantity surveying and more. - Taylor's University
As the top private institution in Malaysia and Southeast Asia, Taylor’s University is a premier choice for many students pursuing their diplomas. Diploma programmes are offered under Taylor’s College and include accounting, business, communication, early childhood education, information technology and interior design.
- Sources
- The Star - Malaysia recorded 5.92 million graduates in 2022, says Statistics Dept















